Blog post by Samuel Gagnon and Pia Blake.
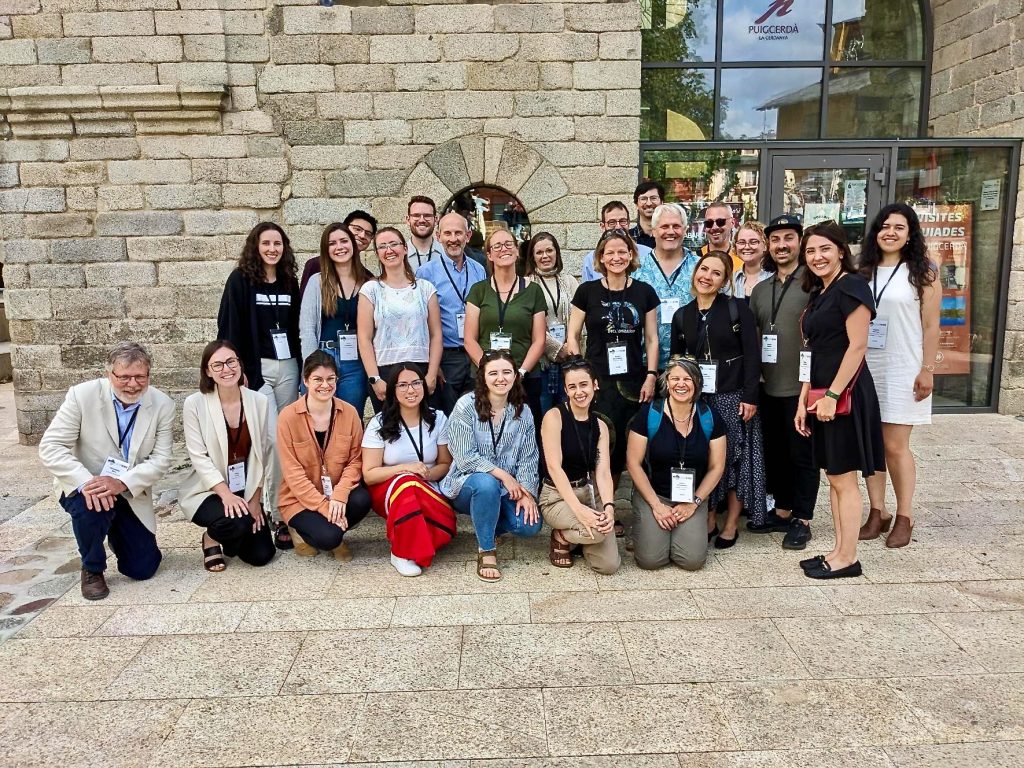
Members of NSERC PermafrostNet gathered in Puigcerdà, Spain, last week for the 6th European Conference on Permafrost (EUCOP 2023). The conference brought together nearly 500 permafrost scientists from all over the world and covered a wide range of permafrost topics from research to engineering and outreach. It was a real treat to have an entire week dedicated to permafrost, something that had not happened since the last EUCOP in 2018. The relatively small number of attendants combined with the proximity that a smaller town offers were the perfect ingredients to renew and create new partnerships, exchange ideas in a casual atmosphere, and create a sense of community.
During the week, scientists attended lectures, participated in topical sessions, and discussed at ‘beer, poster, and cheese’ sessions (yes, that’s the official order from the program!). The quality and variety of presentations were outstanding, and Canadian researchers once again showed the relevance of their work and their know-how to their international colleagues. Many PermafrostNet members distinguished themselves by giving exceptional talks to the assembled participants, including Tabatha Rahman (ULaval), Hannah Macdonell (UCarleton), Adam Kirkwood (ULaval), Mahya Roustaei (UAlberta), Emma Street (UVic), and Toni Lewkowicz (UOttawa), while many others gave poster presentations.
Rounding out the week was a series of day-long field excursions on a range of topics. Participants could learn about the anthropogenic history of the region, the geological history, or explore the mountain peaks surrounding Puigcerdà in the eastern Pyrenees (Cerdanya, Núria, Andorra).
The week flew by and was inspiring and motivating. Many thanks to the organisers who worked tirelessly and pulled off an amazing conference! We look forward to welcoming all to the International Conference on Permafrost (ICOP2024) next year in Whitehorse.
In the meantime, please submit an abstract or join us at the permafrost session – Exploring the Roles of Ground Ice on Permafrost Dynamics at AGU23 on 11-15 December in San Francisco.